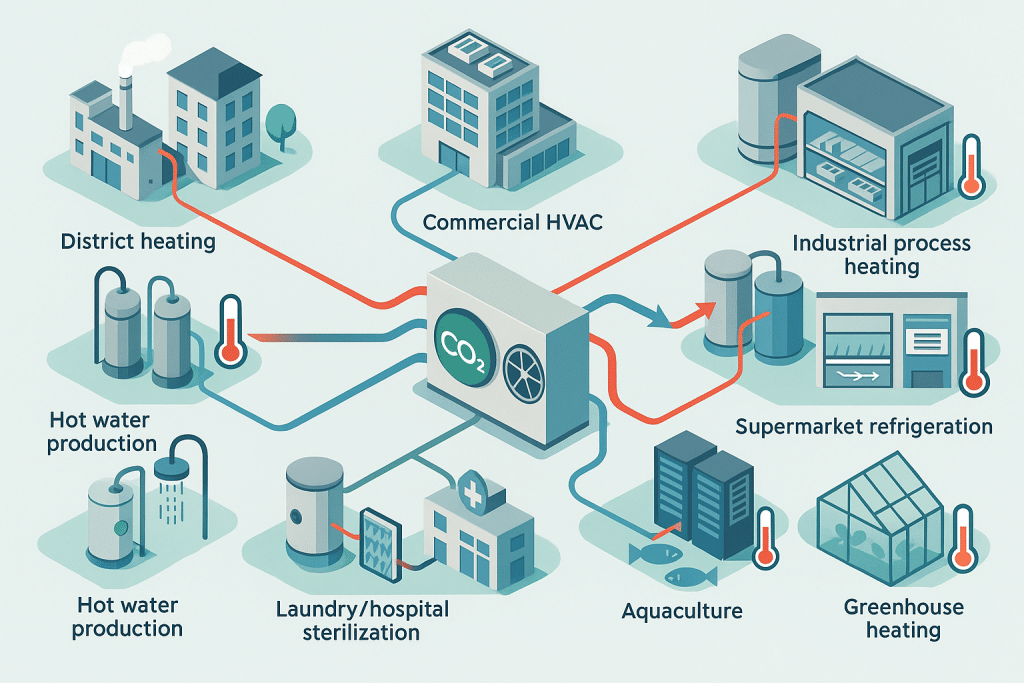
Top Applications of CO2 Heat Pump Technology in Modern Industry
As industries worldwide face mounting pressure to reduce carbon footprints and improve energy efficiency, a revolutionary technology is stepping into the spotlight: the CO2 heat pump.
Unlike conventional heating systems that depend on fossil fuels, a CO₂ heat pump utilizes carbon dioxide as a natural refrigerant to deliver sustainable, high-efficiency thermal energy. Its distinctive characteristics make it well-suited for a broad spectrum of demanding industrial applications.
Why is CO2 the Refrigerant of the Future
At the heart of this technology’s strength is its refrigerant. Unlike conventional synthetic refrigerants with high Global Warming Potential (GWP), CO2 (R744) is a natural substance with a GWP of 1 and zero Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP). This makes it an environmentally superior choice, especially as global regulations rapidly phase out harmful hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs).
Furthermore, a CO2 heat pump can operate at significantly higher coefficients of performance (COP), often delivering 3 to 5 units of heat for every unit of electricity consumed. This high efficiency, combined with the ability to run on renewable electricity, makes it a powerful tool for decarbonization of industrial thermal processes.
Key Industrial Applications: Making the Switch
Here are some of the top industrial sectors where CO2 heat pump technology is making a substantial impact:
1. Food and Beverage Processing
The dairy, meat, and brewing industries require simultaneous heating for pasteurization, cleaning, and bottling, and cooling for process chilling and storage. A CO₂ heat pump uniquely delivers both functions within a single system, capturing waste heat from cooling processes and upgrading it into valuable high-grade heat. This drastically reduces energy costs and greenhouse gas emissions in energy-intensive operations.
2. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
These sectors require precise temperature control for various reactions, distillation, and drying processes. The ability of CO2 heat pumps to deliver consistent and reliable high-temperature heat (often beyond 90°C) makes them perfect for replacing steam boilers for lower-temperature duties, enhancing process safety, and eliminating on-site combustion.
3. Pulp and Paper Production
The paper-making process involves extensive drying, which consumes vast amounts of thermal energy. Integrating a CO2 heat pump to recover low-grade waste heat from exhaust streams and upgrading it to usable temperatures for drying cylinders or pre-heating water presents a massive opportunity for energy savings and operational cost reduction.
4. Automotive and Metal Finishing
Paint shops in the automotive industry require heated water for paint baths and chilled water for paint booth condensation. A CO2 heat pump system efficiently manages this dual demand, ensuring optimal painting conditions while slashing energy consumption compared to running separate heating and cooling systems.
5. District Heating and Commercial Buildings
Large-scale heat pumps, while not confined to one industry, are gaining traction as a solution for supplying carbon-neutral heat to multiple buildings. Using a CO2 heat pump allows utilities to draw heat from ambient air, water, or industrial waste sources, providing a sustainable alternative to gas or coal-fired district heating plants.
The Future is Efficient and Sustainable
The versatility and efficiency of CO2 heat pump technology position it as a cornerstone of modern industrial energy strategy. Across industries ranging from textiles to marine, their ability to supply clean, affordable, and consistent thermal energy is enabling new standards of sustainability and operational excellence.
Interested in discovering how this transformative technology can redefine your industrial heating and cooling processes? Connect with Triveni Turbines to explore sustainable solutions tailored to your specific needs.